Autonomous Vehicles: Latest Developments and Challenges Ahead
Explore the latest developments and challenges in autonomous vehicles. Learn about their benefits, applications, and future trends in transportation.
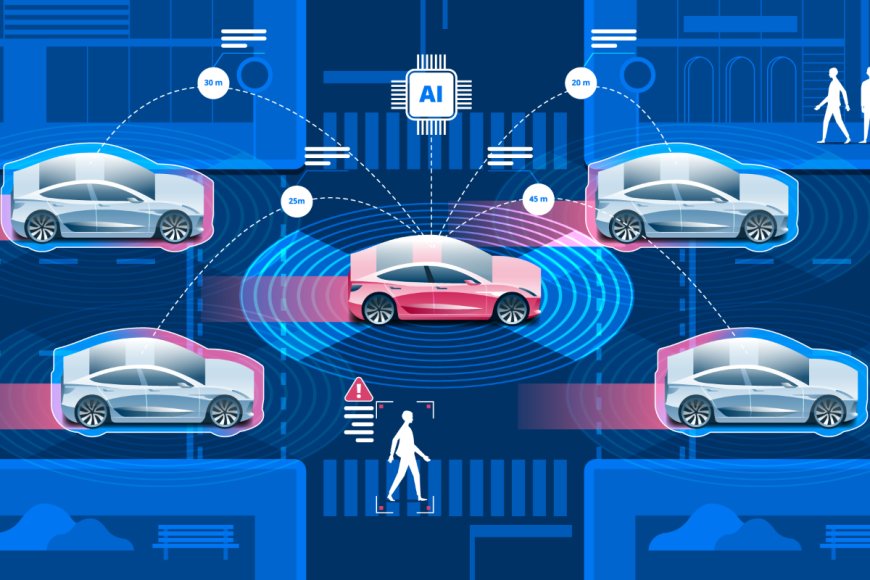
Introduction to Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) and Their Significance
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are revolutionizing the way we think about transportation. These self-driving cars, trucks, and buses promise to make our roads safer, reduce traffic congestion, and lower emissions. However, the journey to fully autonomous vehicles is filled with technological advancements and ongoing challenges. This article will explore the latest developments in AV technology, their applications, benefits, and the hurdles that lie ahead.
1. Understanding
a. What Are Autonomous Vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles are cars, trucks, or buses that can drive themselves without human intervention. The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation).
- Level 0: No automation. The driver performs all driving tasks.
- Level 1: Driver assistance. The vehicle has some driving assist features, like cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial automation. The vehicle can control steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must remain fully attentive.
- Level 3: Conditional automation. The vehicle can manage most aspects of driving, but the driver must be ready to take control.
- Level 4: High automation. The vehicle can perform all driving functions under certain conditions.
- Level 5: Full automation. The vehicle can drive itself under all conditions without human intervention.
b. The History of Self-Driving Technology
The concept of self-driving cars has been around for decades, but significant milestones have occurred in recent years. In the 1980s, researchers at Carnegie Mellon University developed the first autonomous vehicle, the Navlab. In 2004, the DARPA Grand Challenge spurred innovation in self-driving technology. Companies like Google (now Waymo) and Tesla have since made substantial progress, with Waymo launching the first commercial robotaxi service in 2018.
c. Key Components of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles rely on several key components to navigate and make decisions:
- Sensors: These devices collect data about the vehicle's surroundings.
- Cameras: They provide visual information to the vehicle's AI system.
- LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser beams to create a 3D map of the environment.
- RADAR (Radio Detection and Ranging): It uses radio waves to detect objects and measure their distance and speed.
- AI Algorithms: These complex programs analyze data from sensors, cameras, LIDAR, and RADAR to make driving decisions.
2. Latest Developments in Autonomous Vehicle Technology
a. Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the heart of autonomous vehicle technology. AI helps AVs navigate, make decisions, and predict potential hazards. Recent advancements in AI have improved the accuracy and speed of these processes, making AVs safer and more reliable.
b. Improved Sensor Technology
Sensors are crucial for AVs to detect objects and understand their surroundings. Recent improvements in sensor technology have enhanced the accuracy and range of these devices. For example, LIDAR systems now offer higher resolution and better performance in various weather conditions.
c. V2X Communication
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication allows AVs to share real-time information with other vehicles, infrastructure, and even pedestrians. This technology helps AVs make better decisions by providing a broader view of the traffic environment. V2X communication is essential for creating a connected and cooperative transportation system.
3. Applications of Autonomous Vehicles
a. Ride-Sharing and Robotaxis
Companies like Waymo and Cruise are leading the way in ride-sharing and robotaxis. These services use AVs to provide on-demand transportation, reducing the need for personal car ownership and easing traffic congestion. Waymo's robotaxi service in Phoenix, Arizona, is a prime example of this application.
b. Autonomous Freight and Logistics
Self-driving trucks are transforming the freight and logistics industry. These AVs can transport goods more efficiently, reducing costs and improving delivery times. Companies like TuSimple and Embark are developing autonomous trucks for long-haul freight transportation.
c. Public Transportation
Autonomous buses and shuttles are being tested in urban areas to improve public transportation. These AVs can operate on fixed routes, providing a reliable and efficient service. Cities like Las Vegas and Helsinki have already deployed autonomous shuttles for public use.
4. Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
a. Enhanced Road Safety
One of the most significant benefits of AVs is their potential to reduce road accidents. AI-driven decision-making can help AVs avoid collisions and navigate safely, even in complex traffic situations. This could lead to a significant decrease in traffic fatalities and injuries.
b. Increased Accessibility
AVs can provide mobility for elderly and disabled individuals who may not be able to drive traditional vehicles. This increased accessibility can improve the quality of life for many people, allowing them to live more independently.
c. Environmental Impact
AVs can have a positive environmental impact by improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. Electric AVs, in particular, can help decrease greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable future.
5. Challenges Facing Autonomous Vehicles
a. Regulatory and Legal Issues
Navigating the complex web of laws and standards across different regions is a significant challenge for AVs. Regulatory frameworks need to be established to ensure the safe and ethical deployment of AVs. This includes addressing liability issues in case of accidents involving AVs.
b. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
AVs collect and transmit a vast amount of data, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting vehicle and passenger data from cyber threats is crucial. Companies must implement robust security measures to safeguard this information.
c. Ethical Dilemmas in Decision-Making
AVs face ethical dilemmas in critical scenarios, such as deciding between the safety of passengers and pedestrians. Addressing these moral questions is essential for the responsible development and deployment of AVs. Ethical guidelines and standards need to be established to guide AV decision-making.
6. Infrastructure Requirements for Autonomous Vehicles
a. Smart Roads and Traffic Systems
Upgrading infrastructure to support AVs is necessary for their successful deployment. Smart roads and traffic systems can provide real-time information to AVs, helping them navigate more efficiently. This includes installing sensors, cameras, and communication devices along roadways.
b. Urban Planning and Design
Integrating AVs into city layouts requires careful urban planning and design. Cities need to create dedicated lanes, charging stations, and parking areas for AVs. This will help ensure that AVs can operate smoothly within urban environments.
c. Charging Stations for Electric AVs
Expanding the infrastructure for electric AVs is essential for sustainability. Charging stations need to be widely available to support the growing number of electric AVs. This includes installing fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas.
7. Public Perception and Adoption
a. Trust in Autonomous Technology
Overcoming skepticism and building confidence in autonomous technology is crucial for its widespread adoption. People need to trust that AVs are safe and reliable before they will accept them as a viable transportation option.
b. Education and Awareness Campaigns
Informing the public about the benefits and safety of AVs is essential for their acceptance. Education and awareness campaigns can help dispel myths and misconceptions about AVs, encouraging more people to embrace this technology.
c. Addressing Job Displacement Concerns
The adoption of AVs could impact driving-related professions, leading to job displacement. Addressing these concerns is important for a smooth transition. This includes providing retraining programs and supporting affected workers as they adapt to new roles.
8. The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
a. Fully Autonomous Systems (Level 5)
Progress towards complete autonomy (Level 5) is a significant goal for the AV industry. Achieving this level of automation will require further advancements in technology, infrastructure, and regulatory frameworks.
b. Integration with Smart Cities
Autonomous vehicles will play a crucial role in connected urban ecosystems. Integrating AVs with smart cities can create a more efficient and sustainable transportation system. This includes coordinating AVs with public transportation, traffic management systems, and other smart city technologies.
c. Innovations in Energy Efficiency
Combining AV technology with renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable future. Innovations in energy efficiency can help reduce the environmental impact of AVs, making them a more eco-friendly transportation option.
9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Autonomous Vehicles
a. Waymo’s Robotaxi Service
Waymo's robotaxi service in Phoenix, Arizona, is a prime example of successful AV deployment. The company has achieved significant milestones in commercial AV operations, providing a reliable and safe ride-sharing service.
b. Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD)
Tesla's Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) systems have evolved significantly, offering advanced driver assistance features. However, these systems still have limitations and require driver supervision, highlighting the ongoing challenges in achieving full autonomy.
c. Autonomous Trucks in Logistics
Real-world applications of autonomous trucks in logistics have shown promising results. Companies like TuSimple and Embark are demonstrating the efficiency improvements and cost savings that autonomous freight transportation can provide.
d. Key Takeaways on Autonomous Vehicles
In summary, autonomous vehicles offer numerous benefits, including enhanced road safety, increased accessibility, and environmental sustainability. However, challenges such as regulatory issues, data privacy concerns, and ethical dilemmas need to be addressed. Collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and society is essential for the successful deployment of AVs.
Conclusion
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to transform transportation, making our roads safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly. Continued innovation and responsible adoption are crucial for realizing the full benefits of this technology. As we move forward, it is essential to address the challenges and work together to create a future where AVs play a central role in our daily lives.
Frequenly Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are autonomous vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles are cars, trucks, or buses that can drive themselves without human intervention. They use sensors, cameras, LIDAR, RADAR, and AI algorithms to navigate and make decisions.
2. What are the levels of automation in autonomous vehicles?
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation).
3. What are the key components of autonomous vehicles?
The key components include sensors, cameras, LIDAR, RADAR, and AI algorithms. These components work together to help the vehicle navigate and make decisions.
4. What are the benefits of autonomous vehicles?
Benefits include enhanced road safety, increased accessibility for elderly and disabled individuals, and a positive environmental impact through improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
5. What are the challenges facing autonomous vehicles?
Challenges include regulatory and legal issues, data privacy and security concerns, and ethical dilemmas in decision-making.
6. How do autonomous vehicles improve road safety?
Autonomous vehicles use AI-driven decision-making to avoid collisions and navigate safely, reducing the number of traffic accidents.
7. What is V2X communication?
V2X (Vehicle-to-everything) communication allows AVs to share real-time information with other vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians, helping them make better decisions.
8. What are the applications of autonomous vehicles?
Applications include ride-sharing and robotaxis, autonomous freight and logistics, and public transportation.
9. What infrastructure is required for autonomous vehicles?
Infrastructure requirements include smart roads and traffic systems, urban planning and design, and charging stations for electric AVs.
10. What is the future of autonomous vehicles?
The future of autonomous vehicles includes progress towards fully autonomous systems (Level 5), integration with smart cities, and innovations in energy efficiency.
What's Your Reaction?








































